Temperatures of over 40°C were predicted for the coming days, but now it looks like it won’t be quite as bad. How reliable are these forecasts? And how accurately are they calculated? Will tomorrow be the perfect weather to play at https://bizzocasino.com/?
How is the weather predicted today?
To make a weather forecast, meteorologists look at weather models. Weather models, in turn, are the result of complex calculations performed by large, high-performance computers. Put simply, these computers first need data on the current weather situation, which is then calculated taking into account physical processes in the environment in order to predict the weather in the future.
How accurately are current weather conditions measured?
First, data on the initial state of the weather is required. This is recorded using various measuring instruments and methods:
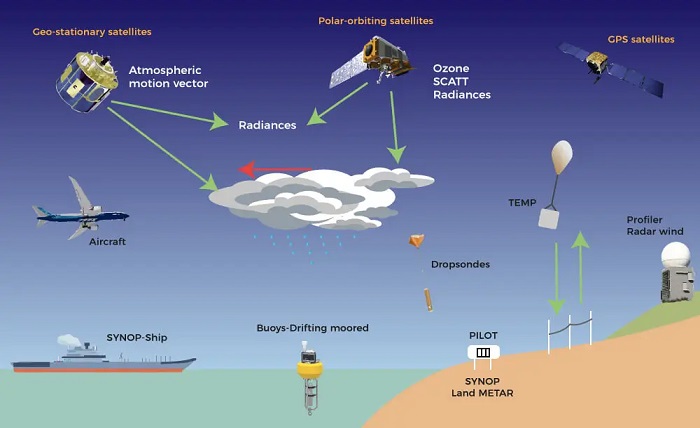
There are ground measuring stations all over the world that collect a wide variety of data, such as the current temperature, wind speed, air pressure, and humidity for the respective location.
So-called precipitation radars measure the water content of a cloud to later conclude possible precipitation (rain, hail, and snow).
Even various ships and buoys in the sea are equipped with measuring devices.
But data is not only collected on the ground. In order to calculate more accurate weather models, we also need data from above. This is provided by commercial aircraft, radiosondes (weather balloons that ascend to an altitude of 20-30 km), and even satellites, which send images and data from space to ground stations. The latter were first used in the 1960s and 1970s and are particularly important for obtaining sufficient data from the southern hemisphere, where there are not as many measuring stations.
The current state of the weather is therefore always known, in some places with great precision, in others with less precision.
The actual data is only one part of creating weather models. “Some of you may be familiar with the measuring stations that you can set up in your garden at home. These provide measurements of the current weather conditions, but they cannot make forecasts. There is much more to it than you might think,” says Luca Mathias. Among other things, all physical processes in the atmosphere and on the ground must also be taken into account. These include, for example, the physical relationships between air temperature, air pressure, wind speed, and humidity. Then there are processes such as cloud formation. Many of these parameters are calculated using so-called partial differential equations, which are quite complicated. Today, however, these calculations do not have to be done by physicists, mathematicians, or meteorologists, but are performed by high-performance computers.
How are weather models actually created?
You can imagine it like this: the entire globe is covered with a three-dimensional grid. This grid can be finely or coarsely meshed, depending on how small or large the area is for which you want to make a prediction. The grid also extends upwards, because there are important interactions and measurements in the atmosphere that need to be taken into account. The larger the area for which you want to calculate a model, the further you have to reach into the atmosphere. Global models utilize satellite data to examine measurement points up to 80 km above the Earth’s surface. By comparison, aircraft only fly up to an altitude of 15 km.
Each grid is therefore several kilometers wide, long, and high. For some grids, the current weather is known with great precision, while for others, it is known less accurately.
Values are then created for each intersection point in the grid, which are incorporated into the mathematical formulas. However, measurements cannot be taken at every point. For grid points for which no measurements are available, data must be “filled in” using mathematical methods. These are usually based on previous model calculations and are combined with measurements from neighboring grid cells.